Labels found on chemical or biological products contain valuable information, namely concerning the danger that they represent. With the creation of laws and standards concerning the labelling of hazardous products, the number of cases of injuries and even deaths linked to household products or hazardous products used at work has considerably decreased.
Legislation governing hazardous products depends on the product type, application and use. I will address household products in this blog post and the labelling of hazardous materials used at work in a separate post.
Household products
Legislation: Requirements from the Consumer Chemicals and Containers Regulations, 2001 (CCCR, 2001) of the Hazardous Products Act
Simplified as much as possible, the information on household products was designed according to the variety of high-risk end-users. In this sense, the hazard symbols are particularly efficient. Who here has never joked about “skulls” or “skeleton hands” as a kid? Despite this, we knew that this represented a danger (and that was the point!) and that we shouldn’t touch these products. Moreover, whatever the language used on the label, the symbols can be understood by people of all languages. This all aims to protect as many people as possible.
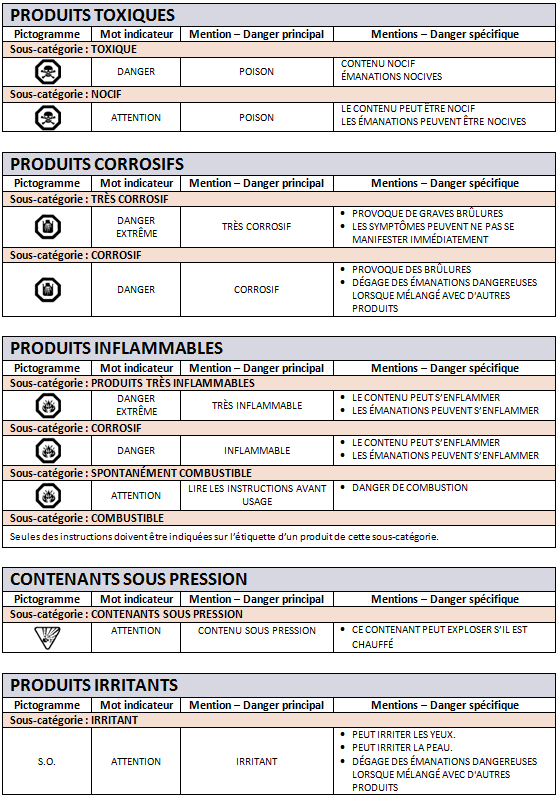
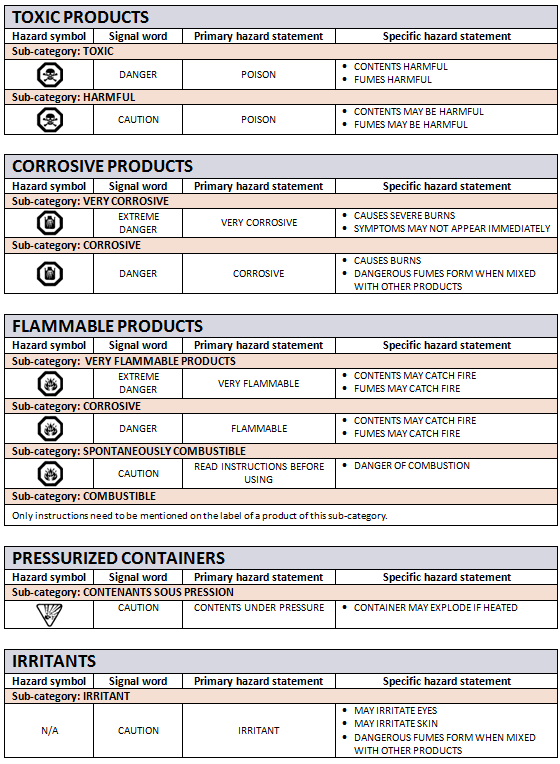
Regarding the labelling of products, the CCCR has created five categories of hazardous products. According to the law, hazard information must contain a hazard symbol (when this is the case) and a signal word to warn about possible risks associated with the product. With the hazard symbol and signal word there is also a primary hazard statement and a specific hazard statement. You will find all of this information in the table below. Although I did not specify in my table, the law also requires labels to mention instructions (for example, “Do not swallow”) and first aid statements.
For further information concerning the legislation in labelling of household products, please visit one of the websites below: